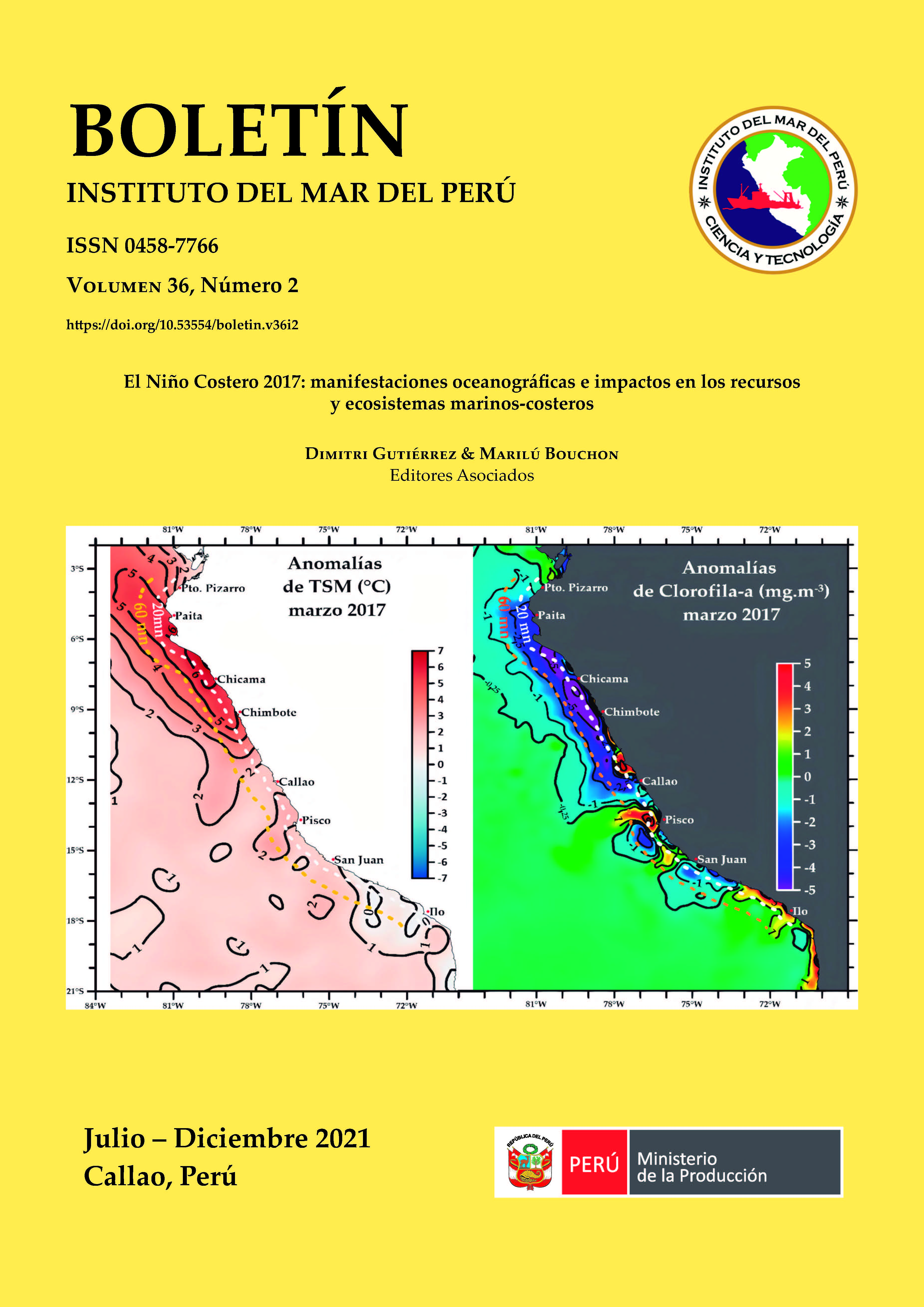
Equatorial Kelvin waves and coastal-trapped waves occurred during El Niño 2015/16 and El Niño Costero 2017 off Peru
comparison between simulations and observations.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53554/boletin.v36i2.342Keywords:
Ondas de Kelvin, El Niño costeroAbstract
The frequent arrival of downwelling Kelvin waves in the Eastern Equatorial
Pacific altered the Peruvian Upwelling Ecosystem (PUE) thus affecting the marine ecosystem and hydrology
off Peru. Therefore, we aim to compare the propagation of the Equatorial Kelvin Waves (EKW) during El
Niño 2015/16 and El Niño Costero 2017 (ENC 2017) off Peru through simulation models and observational
data. Our results show that 7 downwelling EKWs (mode 1) propagated along the equator, and then 6 of
them propagated as downwelling Coastal-Trapped Waves (CTW) during EN 2015/16. On the other hand,
during the ENC 2017 off Peru, only one downwelling EKW (mode 1) was propagated. We can conclude that
the downwelling EKWs played a key role in triggering and developing the warming associated with the EN
2015/16 event off Peru, while they had a secondary role during the ENC 2017, just extending the warming,
which was already initiated by other processes.
Downloads
Alternative Metrics
Metrics
References
Barber R T, Chavez F P. 1983. Biological consequences of El Niño. Science. 222(4629): 1203-1210.
Colas F, Capet X, McWilliams J C, Shchepetkin A. 2008. 1997-98 El Niño off Peru: A numerical study. Progress in Oceanography. 79: 138–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2008.10.015
Dewitte B. 2000. Sensitivity of an intermediate ocean–atmosphere coupled model of the tropical Pacific to its oceanic vertical structure. Journal of Climate. 13(13):2363-2388.
Dewitte B, Reverdin G, Maes C. 1999. Vertical structure of an OGCM forced simulation of the tropical Pacific in 1985–1994. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 29: 1542–1570.
Dewitte B, Gushchina D, DuPenhoat Y, Lakeev S. 2002. On the importance of subsurface variability for ENSO simulation and prediction with intermediate coupled models of the Tropical Pacific: A case study for the 1997-1998 El Niño. Geoph. Res. Lett. 29(14): 1666.10.1029/2001GL014452
Dewitte B, Illig S, Parent L, DuPenhoat Y, Gourdeau L Y J, Verron. 2003. Tropical Pacific baroclinic mode contribution and associated long waves for the 1994–1999 period from an assimilation experiment with altimetric data. J. Geophis. Res. 108(C4): 3121.
Dewitte B, Vazquez-Cuervo J, Goubanova K, Illig S, Takahashi K, Cambon G, … Ortlieb L. 2012. Change in El Niño flavours over 1958–2008: Implications for the long-term trend of the upwelling off Peru. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography. 77-80: 143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2012.04.011
Echevin V, Colas F, Espinoza-Morriberon D, Vasquez L, Anculle T, Gutierrez D. 2018. Forcings and Evolution of the 2017 Coastal El Niño Off Northern Peru and Ecuador. Front. Mar. Sci. 5: 367. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00367
ENFEN. 2016. Comité Multisectorial Encargado del Estudio Nacional del Fenómeno El Niño (Informe Técnico Enfen. Año 2, No. 3, marzo 2016: 54 pp.). Lima, Perú. http://enfen.gob.pe/download/informe-tecnico-2016-3/
ENFEN. 2017. El Niño Costero 2017 (Informe Técnico Extraordinario No. 001-2017). Lima, Perú (pp. 1–31). http://www.imarpe.pe/imarpe/archivos/informes/imarpe_inftco_informe__tecnico_extraordinario_001_2017.pdf.
Espinoza-Morriberón D, Echevin V, Colas F, Tam J, Ledesma J, Vásquez L, et al. 2017. Impacts of El Niño events on the Peruvian upwelling system productivity. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 122: 5423–5444. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012439
Espinoza D, Echevin V, Colas F, Gutierrez D, Graco M, Ledesma J, Tam J, Quispe C. 2019. Oxygen Variability during ENSO in the Tropical South Eastern Pacific. Frontiers in Marine Science. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00526
Garreaud R D. 2018. A plausible atmospheric trigger for the 2017 coastal El Niño. Int. J. Climatol. 38: e1296–e1302. doi: 10.1002/joc.5426
Gutiérrez D, Enriquez E, Purca S, Quipúzcoa L, Marquina R, Flores G, Graco M. 2008. Oxygenation episodes on the continental shelf of central Peru: remote forcing and benthic ecosystem response Prog. Oceanogr. 79: 177–189.
Hobday A J, et al. 2016. A hierarchical approach to defining marine heatwaves. Progress in Oceanography. 141: 227-238. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2015.12.014
Illig S, Dewitte B, Ayoub N, duPenhoat Y, Reverdin G, De Mey P, Bonjean F, Lagerloef G S E. 2004. Interannual long equatorial waves in the Tropical Atlantic from a high resolution OGCM experiment in 1981-2000. J. Geophys. Res. 109(C2): C02022.
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, Collins W, Deaven D, Gandin L, Iredell M, Saha S, White G, Woollen J, Zhu Y, Leetmaa A, Reynolds R, Chelliah M, Ebisuzaki W, Higgins W, Janowiak J, Mo K C, Ropelewski C, Wang J, Jenne R, Joseph D. 1996. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 77: 437-471.
Kessler W S, McPhaden M J. 1995. Oceanic equatorial waves and the 1991–1993 El Niño. J. Clim. 8: 1758–1774.
Kessler W S, McPhaden M J, Weickmann K M. 1995. Forcing of intraseasonal Kelvin waves in the equatorial Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 100: 10,613–10,631. doi:10.1029/95JC00382
King B, Stone M, Zhang H P, Gerkema T, Marder M, Scott R B, Swinney H L. 2012. Buoyancy frequency profiles and internal semidiurnal tide turning depths in the oceans. Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 117, C04008, doi:10.1029/2011JC007681
NOAA. 2019. CPC: Oceanic EL Niño Index. Retrieved from http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/products/analysis_monitoring/ensostuff/ensoyears.shtml
Picaut J, M. Ioualalen M, Menkes C, Delcroix T, McPhaden M J. 1996. Mechanism of the Zonal Displacements of the Pacific Warm Pool: Implications for ENSO. Science. 274: 1486-1489.
Quispe-Ccalluari C, Tam J, Demarcq H, Chamorro A, Espinoza-Morriberón D, Romero C, Dominguez N, Ramos J, Oliveros-Ramos R. 2018. An index of coastal thermal effects of El Niño Southern Oscillation on the Peruvian Upwelling Ecosystem. Int. J. Climatol. 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5493
Reynolds R W, Smith T M, Liu C, Chelton D B, Casey K S, Schlax M G. 2007. Daily high-resolution blended analyses for sea surface temperature. J. Climate. 20: 5473-5496.
Shaffer G, Pizarro O, Djurfeldt L, Salinas S, Ruttlant J. 1997. Circulation and low frequency variability near the Chilean coast: remotely forced fluctuations during the 1991–1992 El Niño. J. Physical Oceanography. 27: 217–235.
Ramírez I J, Briones F. 2017. Understanding the El Niño Costero of 2017: The definition problem and challenges of climate forecasting and disaster responses. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science. 8: 489–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13753-017-0151-8
Takahashi K, Martinez A G. 2017. The very strong coastal El Niño in 1925 in the far-eastern Pacific. Climate Dynamics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3702-1
Takahashi K, Aliaga N, Ávalos G, Bouchon M, Castro A, Cruzado L, Dewittw B, Quispe N. 2018. The 2017 coastal El Niño. In: State of the climate in 2017. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 99(8): S210-S242. Doi:10.1175/2018bammsstateoftheclimate.1
Zebiak S E, Cane M A. 1987. A model El Niño southern oscillation. Mon. Weather Rev. 115: 2262– 2278.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Boletin Instituto del Mar del Perú

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
© Bol Inst Mar Perú. La revista retiene los derechos patrimoniales de los autores con la finalidad de garantizar el acceso abierto de los manuscritos.
Todos los manuscritos publicados en la revista se distribuyen bajo la licencia “Creative Commons Atribución - NoComercial - CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional” (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0). Implica que autores y lectores pueden de forma gratuita descargar, almacenar, copiar, redistribuir, remezclar, transformar o generar obras derivadas a partir del manuscrito, siempre y cuando mencionen la fuente primaria de publicación y la autoría del manuscrito, así como que se realice sin fines comerciales y se distribuya bajo la misma licencia que el original. Puede consultar desde aquí la versión informativa y el texto legal de la licencia.